
SEO: Search Engine Optimization Techniques and Types
What is SEO and why is it so important?
Welcome to the ultimate guide on SEO – the secret sauce behind boosting your online presence and driving more traffic to your website. Whether you’re a digital marketing enthusiast or a business owner looking to up your online game, understanding Search Engine Optimization and Marketing is crucial in today’s competitive digital landscape. So, buckle up as we dive into the world of Search Engine Optimization and uncover its best practices, techniques, and types that will help you climb the ranks in search engine results pages!
The success of search engines as businesses relies on the public perceiving their results to be tailored to their needs. As a search engine, such as Google, discovers more links from a certain type of content to a specific resource, it gains confidence in the relevance of that resource for related search queries. This leads to the determination that the resource should receive a high ranking when those queries are made. To aid in this process, there are four main categories of SEO: on-page, off-page, local, and technical. These work together to assist search engines in discovering, crawling, indexing, understanding, and ranking your content.
Best practices and techniques
When it comes to SEO, staying ahead of the game means keeping up with best practices and techniques. One key aspect is optimizing your website’s loading speed – a fast site not only improves user experience but also boosts your search rankings. Another important practice is creating high-quality, relevant content that resonates with your target audience.
Utilizing proper heading tags and meta descriptions can also enhance your site’s visibility in search results. Additionally, incorporating internal linking within your content helps search engines navigate through your site efficiently. Then reporting on why and how a site moves through search results is critical.
Don’t forget about mobile optimization – ensuring that your website is mobile-friendly is essential for ranking well in mobile searches. Lastly, monitoring and analyzing performance metrics using tools like Google Analytics and SEMRush can provide valuable insights for refining your SEO strategies.
Types of SEO such as technical, local, on-page, off-page
When it comes to SEO, there are several different types that play a crucial role in boosting your online presence.
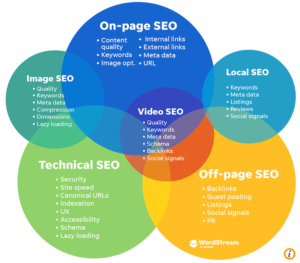 Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of your website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engines. This includes factors like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and structured data.
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of your website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engines. This includes factors like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and structured data.
Local SEO is essential for businesses targeting local customers. It involves optimizing your online presence to attract more foot traffic and leads from specific geographic locations.
On-page SEO revolves around optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic. This includes keyword optimization, meta tags, and high-quality content creation.
Off-page SEO refers to strategies implemented outside of your website to improve its authority and credibility. This includes link building, social media marketing, and influencer collaborations.
Each type of SEO plays a unique role in enhancing your online visibility and driving organic traffic to your website.
Keyword research and four types of keywords
Keywords are a fundamental aspect of Search Engine Marketing that cannot be overlooked. By conducting thorough keyword research and strategically incorporating relevant keywords into your content, you can boost your website’s visibility and attract more organic traffic.
- Informational: A person wanst to find information
- Navigational: Includes searches for a specific site or page
- Commercial: A person wants to investigate brands, products, or services
- Transactional: The searchers want to complete an action (e.g., buy something or sign up)
In the world of Search Engine Optimization, staying up-to-date with the latest best practices and techniques is crucial for success. Whether you focus on technical optimization, local SEO, on-page strategies, or off-page tactics, implementing a comprehensive strategy tailored to your specific needs is essential for improving your search engine rankings.
Overall, mastering the art of SEO requires dedication, patience, and continuous learning. By following these guidelines and adapting to the ever-evolving landscape of search engine algorithms, you can enhance your online presence and drive valuable traffic to your website. Remember: SEO is not just about ranking high on search engines; it’s about providing value to your audience and delivering an exceptional user experience.
Stay on top of your SEO plan
Monthly SEO Reports sent directly to you
Independent reports to manage consultants, departments, and agencies better from the #1 SEO tracking tool.


















